
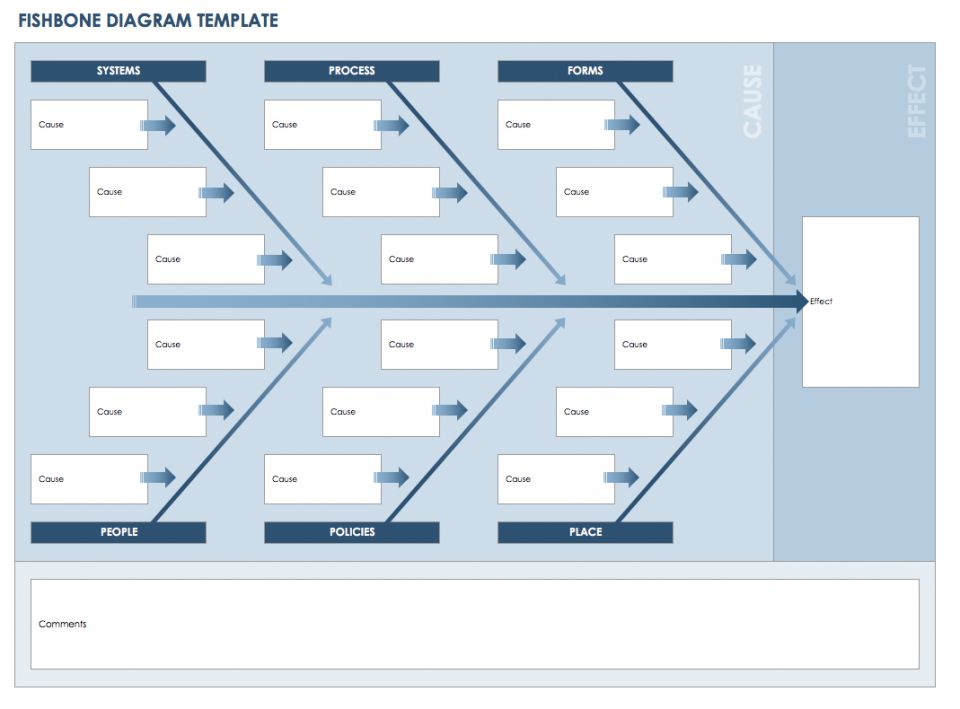
Then team was assembled to find problem root cause. That is not a good affect of this process, isn´t it?įirst what team did, is developed robust method to identify vibrations. It is causing a lot of troubles and reworks. But this vibration does not occur every time part is grinded. There is a problem with vibrations on very precisely grinded surface. What DMAIC tool list to follow during projects? (+template)- read here Fishbone diagram example Rewrite all ideas into the electronic table.

The most frequent idea can be the one with larger influence. Identify priorities and the largest cause out of those ideas.Let team members to explain, why each reason is influencing the problem. But to have different point of views ideas is very important. It is not so important where idea is attached on fishbone. Give team 5 to 10 minutes to write their ideas on stickers.Challenge team members to write at least 3 reasons that problem occurs on each fishbone section. Write your problem into effect part of fishbone. Make sure everyone understands problem prior brainstorming.Ask them if they think to have somebody else in the team. Start with members you know, they are important. To identify problem root cause it is crucial to have right team members. With is information, we can say that the Ishikawa diagram represents the relationship between defects and their causes so option 3 is correct.How to perform Gemba walk? (+guidline) – read here Follow these steps for successful tool usage.It is frequently used to aid in lean and six-sigma transformations because it allows manufacturers to reduce clutter by identifying the root causes of issues and identifying areas for improvement.By visually sorting possible defect causes, identifying cause and effect relationships, and determining which causes are having the greatest impact on the problem, the Fishbone Diagram enables people to address the problem rather than its symptoms.In the image below, for example, the problem is that 12% of the product fails inspection, and one of the potential causes of this related to the materials is that screws were worn.Using these as prompts to generate hypotheses for the root cause of a problem, you write the potential causes under each of these on the “ribs” of the fish.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
